Vocab list #3
ActiveX-a framework for defining reusable software components that perform a particular function or a set of functions in Microsoft Windows in a way that is independent of the programming language used to implement them.
Client- an application or system that accesses a remote service on another computer system, known as a server, by way of a network.
Cookie-a small piece of text stored on a user's computer by a web browser. A cookie consists of one or more name-value pairs containing bits of information.
Digital Certificate an electronic document which uses a digital signature to bind together a public key with an identity information such as the name of a person or an organization, their address
Domain a field of study that defines a set of common requirements, terminology, and functionality for any software program constructed to solve a problem in the area of computer programming.
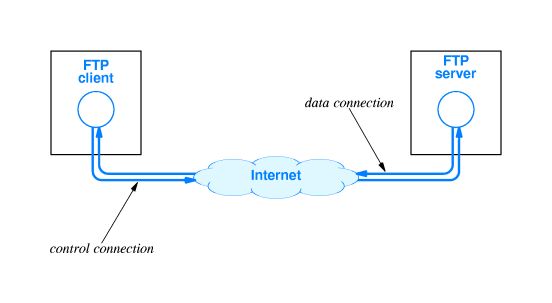
File Transfer Protocol-protocol that allows users to copy files between their local system and any system they can reach on the network.
Geographic ImagingA computer application used to store, view, and analyze geographical information, especially maps.
Hit- Any time a piece of data matches criteria you set. For example, each of the matches from a Yahoo or any other search engine search is called a hit.
Home Page -the URL or local file that automatically loads when a web browser starts or when the browser's "home" button is pressed
Hypertext Markup Language- the predominant markup language for web pages. It provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists etc as well as for links, quotes, and other items.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol- an Application Layer protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems.
Internet Protocol Address-a numerical label that is assigned to devices participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication between its nodes.
Internet Service Provider-A company or organisation that offers Internet access to customers for a fee. Some ISPs offer hosting of websites and website design and promotion services as well.
Mosaic -the art of creating images with an assemblage of small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials. It may be a technique of decorative art, an aspect of interior decoration, or of cultural and spiritual significance as in a cathedral
Podcasta series of digital media files that are released episodically and often downloaded through web syndication.
Portal-In computer-generated imagery and real-time 3D computer graphics, portal rendering is an algorithm for visibility determination.
Really Simple SyndicationAllows you to collect news and postings from newspapers, blogs, libraries, etc. and read them in one place. Popular RSS feed readers include Google Reader and Bloglines.
Social Networking Site-A social network service focuses on building and reflecting of social networks or social relations among people.
Uniform Resource Locator-the address of a web page on the world wide web
Web 2.0-commonly associated with web applications that facilitate interactive information sharing, interoperability, user-centered design,
Web Cache- A web cache stores copies of documents passing through it; subsequent requests may be satisfied from the cache if certain conditions are met.
Website- a computer connected to the internet that maintains a series of web pages on the World Wide Web
webapp-a web application is an application that is accessed via a web browser over a network such as the Internet or an intranet.
Wiki- a website that allows the easy creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language.
Blog- read, write, or edit a shared on-line journal
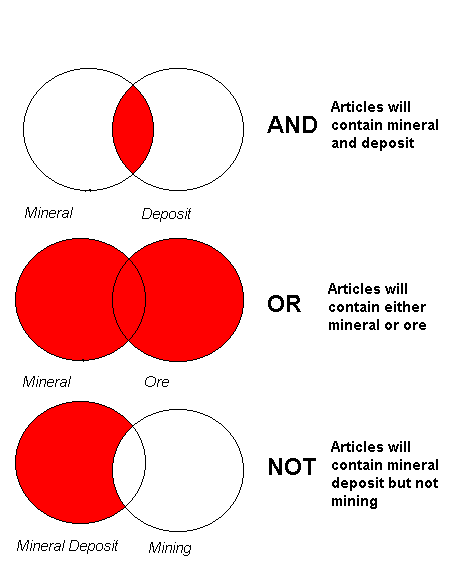
boolean Logic-a system of symbolic logic devised by George Boole; used in computers
copyright-a document granting exclusive right to publish and sell literary or musical or artistic work
Directories-as used in computing and telephony, refers to a repository or database of information which is heavily optimized for reading, under the assumption that data updates are very rare compared to data reads.
Feed- the process for conceptual development of processing industry projects. Example of processing industry are upstream, petrochemical, refining, pharmaceutical.
Secure Sockets Layer- are cryptographic protocols that provide security for communications over networks such as the Internet. TLS and SSL encrypt the segments of network connections at the Transport Layer end-to-end.